Types of Home Heating Systems (2023 Guide)
by Admin
Posted on 04-11-2023 12:29 PM

One of the most common types of heating systems is the forced-air or central heating system.
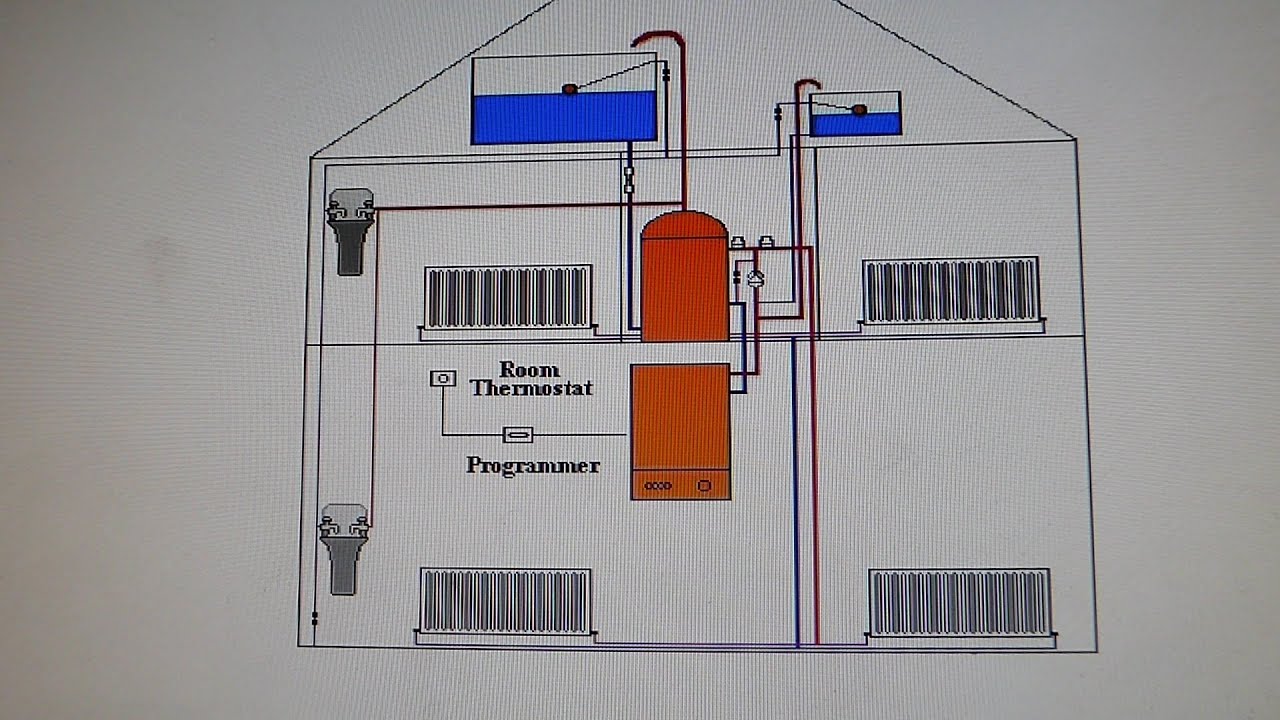 The furnace heats air and delivers it into the entire house through the ducting system along with the vents and registers. A standard forced-air system uses one central thermostat to control the temperature of the whole house. If you have a home with multiple levels, the upper rooms are often warmer than the lower ones. In addition, if you have unoccupied or unused rooms, the forced air system still sends heat into those rooms. As a result, it wastes energy and money.
The furnace heats air and delivers it into the entire house through the ducting system along with the vents and registers. A standard forced-air system uses one central thermostat to control the temperature of the whole house. If you have a home with multiple levels, the upper rooms are often warmer than the lower ones. In addition, if you have unoccupied or unused rooms, the forced air system still sends heat into those rooms. As a result, it wastes energy and money.
From november to march, the temps in kansas city hover around freezing. There are so many different types of home heating and cooling systems that it can feel overwhelming when researching your next home upgrade. Heating your home is the costliest utility expense for homes in north america making up about 30 percent of all utilities paid annually. Luckily, maintaining and replacing old equipment with newer energy-efficient models can help decrease these costs significantly. Shopping for a new heating system is also an opportunity to reduce your home’s carbon footprint for the next 15 or 20 years by switching from fossil fuel to electricity-powered hvac solutions like electric furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps.
Overall, most central heating systems can be boiled down to one of three major types. These all function differently and some are more efficient depending on where they are placed or how they connect to the rest of the home. Remember that heating systems have to be tailored to the building they are placed in, so there is no such thing as a one-size-fits-all system. Some will be more efficient in buildings below a certain size, while others might need more work to set up in smaller spaces.
4. In-Floor Radiant Heating
An electrically generated heat source for individual rooms and areas, cove heating employs radiant heat to warm the room and objects in the room.
 Coined “cove heating” because it is installed where the cove used to be in older room designs, individual heating units are mounted on the wall 2 1/2 to 4″ below the ceiling, allowing homeowners unrestricted use of floor space. View more information.
Coined “cove heating” because it is installed where the cove used to be in older room designs, individual heating units are mounted on the wall 2 1/2 to 4″ below the ceiling, allowing homeowners unrestricted use of floor space. View more information.
That’s the appeal of radiant floor heating, says this old house plumbing and heating expert richard trethewey, who has long been a fan. “it’s truly invisible,” he says. But a radiant heat system has more than just aesthetics going for it. It’s also a highly efficient way to heat a house, increasing comfort as it reduces energy costs. In a radiant setup, the warmth is supplied by hot-water tubes or electric wires buried underneath the floor. As the invisible waves of thermal radiation rise from below, they warm up any objects they strike, which radiate that captured heat in turn.
Radiant heating systems use hot water or electricity to heat tubes in the floor, ceiling, or walls. These systems can use a variety of fuel sources, including gas and electricity. Radiant heating creates even indoor temperature and a pleasant warmth in the floor that many homeowners like. However, these systems can be expensive to repair when something goes wrong. At the moment, radiant heating is sometimes used in bathrooms but may not be found throughout the rest of the house.
on average, a u. S. Household spends about $700 on heating using natural gas and around $1,700 on heating using heating oil. Most of the time, natural gas is the most efficient means of heating the home, which is why most american households use it. Household heating systems: although several different types of fuels are available to heat our homes, nearly half of us use natural gas. | source : buildings energy data book 2011, 2. 1. 1 residential primary energy consumption, by year and fuel type (quadrillion btu and percent of total). While heating systems and fuel types can make a big difference, the best way to save energy and money is by properly maintaining your equipment and insulating your home.
Heating and cooling systems have three basic elements—a source of warm or cool air, a method of sending the heated or cooled air into your living space, and a way to control the temperature in your home. The thermostat recognizes when the temperature is too hot or too cold, and turns the system on and off to maintain your temperature based on your preferences. A furnace, air conditioner, or heat pump will take in existing air from inside your home, heat or cool it, then push that air back into your living space to achieve the desired temperature. Click here to learn more on ductless mini split.
For those who do not have a central furnace in their home or has one that is having a hard time meeting demand, there are several space heating options available. While it is possible to heat your entire home with electric or kerosene heaters, they are not designed to heat multiple rooms or maintain the temperature over an extended period. Space heaters are intended to be supplemental to a more efficient and more powerful whole-house heating system and most usually found in rooms at the end of the home furthest from the furnace. Radiant kerosene heaters: single room space heaters that use kerosene can release toxic gases into the air if the wrong fuel/air mixture is present.